What Is PBIS?
Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports, often referred to as PBIS is an evidence-based, prevention and intervention framework for establishing a safe and supportive learning environment.
Research supports that when schools implement PBIS with integrity and fidelity, PBIS provides common vision, language and practices used consistently across the school to meet the following outcomes:
- improve school climate
- strengthen relationships
- teach and reinforce expectations through feedback
- increase equitable learning experiences
- decrease office referrals and suspensions
PBIS is a common framework used to address behavior, school climate, and school culture within an integrated Multi-tiered System of Supports (MTSS).
What Does PBIS Look Like?
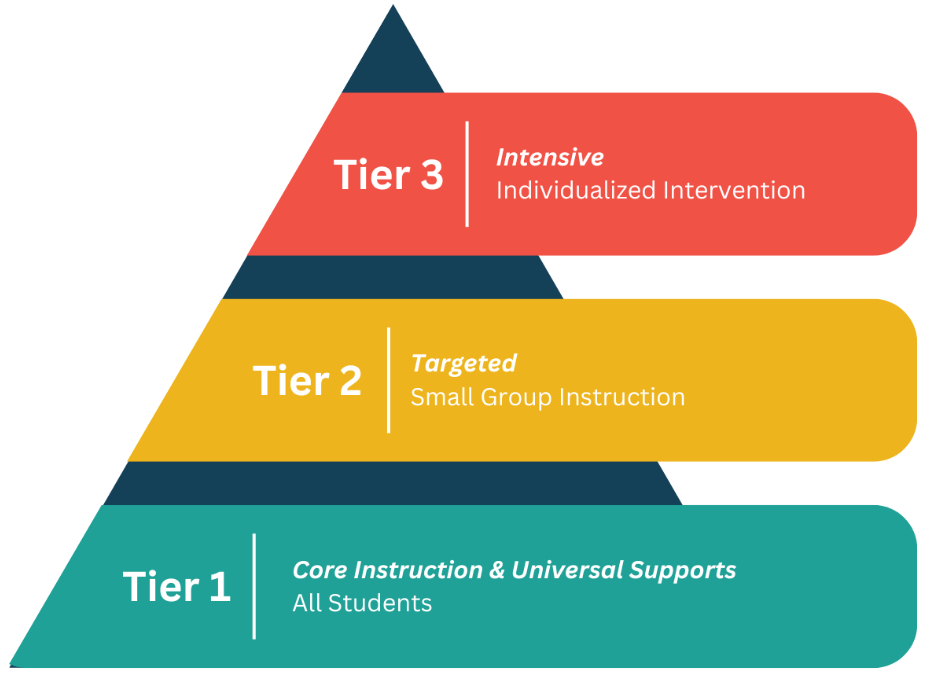
Tier 1
Prevention practices and behavioral instruction is for all students and should meet the needs of at least 80% of students. All students receive Tier 1 universal behavioral instruction regardless of additional support they may receive.
Tier 2
Targeted interventions are for students needing additional behavioral support. Even with a strong Tier 1 system in place, about 10-15% of students may need targeted intervention, in addition to Tier 1 supports, to learn and apply appropriate social and learning behaviors.
Tier 3
Intensive interventions are for individual students who are not responding to Tier 1 and Tier 2 intervention. About 5% of students may need Tier 3 intervention, within the general education setting, such as self-monitoring, a behavior contract or individual counseling and mentoring.
Tier 2 and Tier 3 interventions are typically managed by a team of educators responsible for identifying students in need of intervention, matching the appropriate intervention with the student’s needs, and monitoring student progress.
How Is PBIS Implemented?
The framework of PBIS helps schools and classrooms to organize behavioral instruction, resources, and interventions that are effective and efficient through three integrated elements that support measurable student outcomes.
These three elements include:
- school-wide systems that efficiently and effectively support positive behavior
- data for decision making
- evidence-based practices and interventions to achieve outcomes
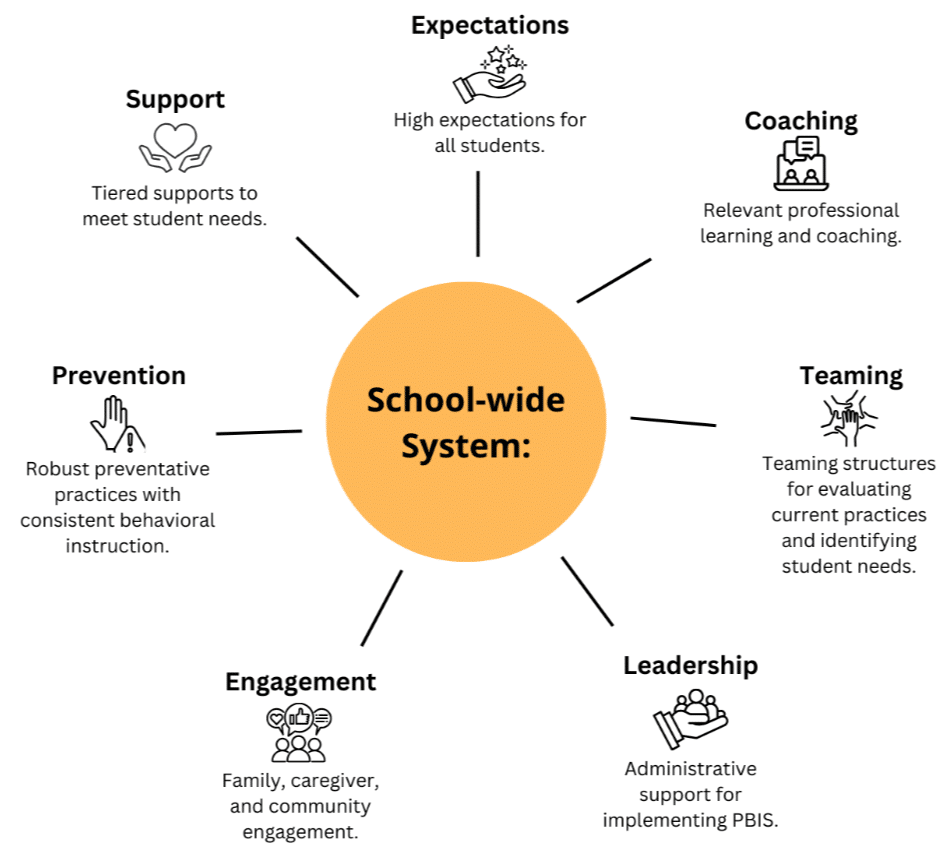
School-Wide System Includes:
- Teaming: Teaming structures for evaluating current practices and identifying student needs
- Prevention: Robust preventative practices with consistent behavioral instruction
- Support: Tiered supports to meet student needs
- Expectations: High expectations for all students
- Coaching: Relevant professional learning and coaching
- Engagement: Family, caregiver, and community engagement
- Leadership: Administrative support for implementing PBIS
Data for Decision Making Includes:
- Developing a decision-making process
- Identifying relevant data points, such as discipline referrals, attendance, and counselor referrals
- Using those data points to determine root cause of behaviors and student needs
- Progress monitoring the effectiveness of tiered behavioral instruction, prevention practices, and interventions
Tier 1 Evidence-Based Practices Include:
- Design: Design effective and organized classroom environments
- Teach: Develop, teach, model, and practice positively-stated school-wide and classroom expectations and agreements
- Plan: Plan and teach predictable classroom routines
- Deliver: Deliver engaging instruction by incorporating students’ background knowledge and experiences
- Engage: Provide multiple opportunities for students to respond to and engage in instruction
- Supervise: Actively supervise students through scanning, moving, and interacting
- Acknowledge: Acknowledge students with behavior specific feedback to ensure they know what they’re doing right
- Prompt: Provide prompts and precorrection to prevent behavioral mistakes
- Correct: Respond to problem behavior with brief, subjective, and calm error correction
- Promote: Promote student voice and seek feedback from students often
How Has PBIS Evolved?
It is important to note that the tenets of PBIS have evolved to recognize that behavior occurs within a cultural context and is also a means of communication.
Therefore, modern PBIS embeds student, caregiver, and community voice to increase awareness of:
- cultural context
- culturally responsive behavioral practices
- intentional focus on educational equity
PBIS Does Not Ignore Problem Behaviors
Rather, PBIS focuses on preventing problems, teaching lifelong behavioral and social skills, and providing students with a safe, caring, and equitable learning environment. In addition, PBIS uses an instructional approach to correct behavior and applies logical consequences consistently and equitably. Discipline is a positive method of teaching desired behaviors while keeping children connected to the school community.
PBIS Is Not a Prize System
While rewards, incentives, and prize programs can be fun ways to teach and acknowledge positive and expected behaviors, they have been a common misuse of PBIS principles in the past. Rewards programs are only effective for long-term behavior change when paired with relevant and consistent behavioral instruction and frequent behavior specific feedback.
A quick trick to determine if rewards and prize programs are effective is to ask students how they received a point/ticket/prize, incentive, etc. If students are not able to communicate a specific behavior they performed to get that reward (e.g. make the connection between cause and effect), it’s likely the rewards program lacks the components of PBIS and may not be an efficient way to teach and sustain long-term behavior change.
PBIS Is Not an Extracurricular Program
PBIS is a school-wide framework for supporting behavioral health across all three tiers of instruction. Therefore, implementing PBIS principles and practices is the responsibility of all school staff, not just a small committee. As a school-wide system addressing behavioral and environmental practices and discipline policies, school administrators should be engaged with PBIS implementation.
Overall
The foundation of PBIS is having a common philosophy on behavior and high expectations for all students, as well as having consistent language and practices across the school so students know what to expect.
The PBIS framework supports:
- prevention strategies
- interventions
- data trend analysis
- discipline considerations
- mitigates disproportionate student discipline outcomes and experiences.
PBIS is most effective when integrated with high quality academic instruction and response to intervention practices and social, emotional, and mental wellness instruction and supports through a multi-tiered system of supports.